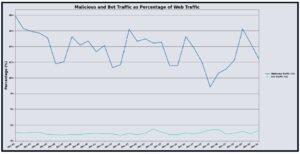
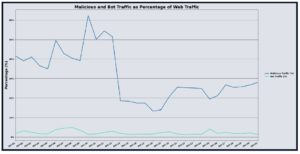
In November 2025, UltraWAF processed approximately 1.82 trillion web requests, a slight decrease of 2.47% compared to October 2025. Of this traffic, 25.50%, roughly 464 billion requests, were identified as malicious, marking a 21.41% reduction in overall malicious volume month over month. Bot-originating traffic, however, rose significantly, accounting for 1.35% of total requests, a 43.79% increase compared to the previous period. These fluctuations suggest continued automated scanning activity amid generally stable customer web traffic volumes.
The 400 Response category showed the largest behavioral change because it experienced an 186.12% increase. The sudden increase in malformed requests points to malicious actors who use deliberately flawed requests to test application parsing and validation mechanisms. The observed behavior leads to more specific attacks on web applications. The Cookie-based threat category was the most common threat at 54.84% followed by Command Injection at 21.00% and Field Format violations at 10.12%. The threat distribution shows that attackers continue to focus on manipulating input data and testing command execution on exposed web application interfaces.
The observed payloads from this month demonstrate various exploitation techniques which include basic command injection and complex framework-specific vulnerabilities. The system detected three main types of attacks which included command injection probes with randomized markers for execution validation and SSRF attempts through image-fetch endpoints and JNDI-based payloads that used Log4Shell-style obfuscated constructs to perform remote lookups. The attacks focused on exploiting known software frameworks and plugins through three different methods which included Apache Struts OGNL injection and elFinder admin interface exploitation and WordPress plugin abuse for unauthorized account creation and file inclusion and remote file access. The system detected multiple probes which used XWiki and Qwiz content-management systems to execute Groovy code and JavaScript for command execution and reflected XSS testing. The observed payloads demonstrate how attackers perform extensive reconnaissance through the entire application infrastructure, starting from web form inputs to backend command execution.
The threat environment during November consisted of ongoing automated scanning operations and attacks on outdated web system components and attackers who used encryption and tokenization to bypass standard filtering systems. The combination of request corruption events with command injection attacks and sophisticated framework exploitation attempts demonstrates how attackers evolve their tactics while requiring better monitoring of payload evolution to detect new attack methods.
Stats at a Glance
- Total Web Requests: 1,820,791,069
- Largest Threat Category: Cookie (54.84%)
- Total WAF Violations: 464,356,880
- Top Three Industry Targeted: Travel/Hospitality (81.47%), Financial (15.68%), Technology/Security (1.35%)
- Total Bot Violations: 23,515,270
- Top Three Source Countries: Great Britain (80.14%), United States (8.15%), France (0.98%)