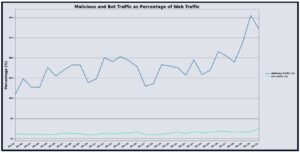
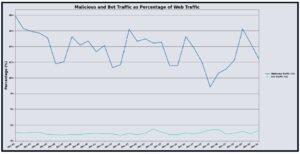
In September 2025, UltraWAF recorded approximately 984 billion requests, a 12.41% decrease from August, indicating a slightly reduced but still substantial request load. Despite this decline, malicious traffic increased, with 73.02% of requests flagged as malicious and bot-originated traffic rising to 3.27% of the total volume. This concurrent rise in malicious activity and bot traffic, despite lower overall requests, suggests that threat actors are actively targeting reachable or newly onboarded application surfaces and event-driven traffic peaks with focused reconnaissance and exploit attempts.
The composition of threats was primarily driven by protocol and input-format-based probes and violations. Invalid RFC violations constituted the largest share of the identified malicious traffic at 56.29%, followed by Cookie-related attacks at 20.94% and Field Format issues at 7.72%. While 70% of tracked threat categories saw a month-over-month decline, high-risk vectors like Buffer Overflow Cookie attacks surged by 107.18%, indicating attackers are exploiting legacy or unpatched software vulnerabilities through HTTP headers. These shifts highlight adversaries focusing on both significant protocol deviations and carefully crafted application-level inputs, moving beyond broad volumetric attacks.
Payloads observed during this period were diverse, technically sophisticated, and heavily obfuscated to evade simple detection. UltraWAF identified automated probes and exploit attempts, including reflected and stored cross-site scripting, union-based SQL injections aimed at extracting database metadata, and server-side request forgery (SSRF) patterns designed to trigger connections to attacker infrastructure. More severe threats included JNDI/LDAP-style lookups resembling Log4Shell, OGNL expressions targeting Apache Struts for remote command execution, php-cgi runtime ini overrides enabling remote code inclusion, and serialized-object payloads exploiting unsafe PHP unserialize chains. Attackers also employed embedded command-injection patterns, obscure control-byte sequences, and long fuzzing payloads with heavy encoding, shell-style expansions, and serialized/gadget-style payloads to bypass filters and provoke outbound connections.
The operational implications emphasize the need for robust application and platform hardening, WAF tuning, and egress control. The diverse payload mix heightens the risk of information disclosure and remote code execution if legacy components or permissive configurations persist. Recommended actions include accelerated patch management for web frameworks and middleware, stricter input validation and output encoding for user-facing parameters, targeted WAF signature updates for JNDI/OGNL and serialized-object patterns and enhanced outbound request monitoring and egress filtering to block attacker callbacks. Prioritizing comprehensive logging, rapid incident triage for high-confidence remote code execution probes and validating secure server configurations—such as disabling runtime ini overrides and unsafe PHP handlers—will significantly reduce the risk of successful compromises.
Stats at a Glance
- Total Web Requests: 984,310,454
- Largest Threat Category: Invalid RFC (56.29%)
- Total WAF Violations: 718,767,522 (a 2.77% increase from August 2025)
- Top Three Industry Targeted: Travel/Hospitality (80.53%), Financial (12.12%), Retail (6.19%)
- Total Bot Violations: 32,205,034 (a 6.64% increase from August 2025)
- Top Three Source Countries: Great Britain (86.17%), United States (5.03%), France (0.98%)